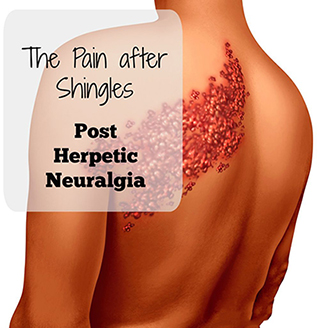
Post Herpetic Neuralgia (Shingles)
Herpes zoster is an infectious disease caused by Varicella-zoster virus. The virus remains dormant in the ganglia, producing no clinically evident disease. In some individuals, the virus may reactivate producing ganglionitis & peripheral neuritis which cause pain characteristic of shingles. This is often called post-herpetic neuralgia. It is most common in thoracic dermatome. It may be very severe and prolonged, particularly in older patients.
The symptoms of postherpetic neuralgia can vary from a mild self-limited problem to a debilitating, constantly burning pain that is exacerbated by light touch, movement, anxiety, and/or temperature change.
The earlier the treatment of Herpes zoster is initiated, the less likely the patient will develop postherpetic neuralgia. Post-herpetic neuralgia is most likely to occur in an older patient, so early and aggressive treatment of this group of patients is mandatory.
Treatment Options
Sympathetic neural blocks suppress the profound sympathetic stimulation caused by ganglionitis & peripheral neuritis. Si it is the treatment of choice to relieve the symptoms of acute herpes zoster as well as to prevent the occurrence of postherpetic neuralgia.
Opioids, antidepressants, anticonvulsants also help to reduce pain. Adjuvants like ice application, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, and vibration, topical lignocaine patches, topical capsaicin are also useful.




